St. Cloud WTF AOP and Biological Filtration Pilot
St. Cloud, MN
Project Overview
The City of St. Cloud currently operates a 24 million-gallon-per-day lime-softening water treatment facility (WTF) that withdraws source water directly from the Mississippi River. The conventional treatment consists of clarification, lime softening, recarbonation, gravity filtration, and disinfection. The WTF experiences seasonal taste and odor (T&O) events during spring runoff and heavy rainfall events and also occasionally observes TTHMs exceeding their own treatment goal in the distribution system. A facility master plan was completed in 2014 and evaluated five alternatives for the future technology upgrade.
Project Details
Date: 2015 – 2016
Client: City of St. Cloud
Key Project Elements
- Development of a Comprehensive Piloting Protocol
- Side-by-Side Evaluation of Peroxone, Ozone, and UV Peroxide
- Side-by-Side Evaluation of Multiple Filter Media
- Achieve Taste & Odor Removal, Disinfection, and DBPs Mitigation
- Profiling Contaminants of Emerging Concerns
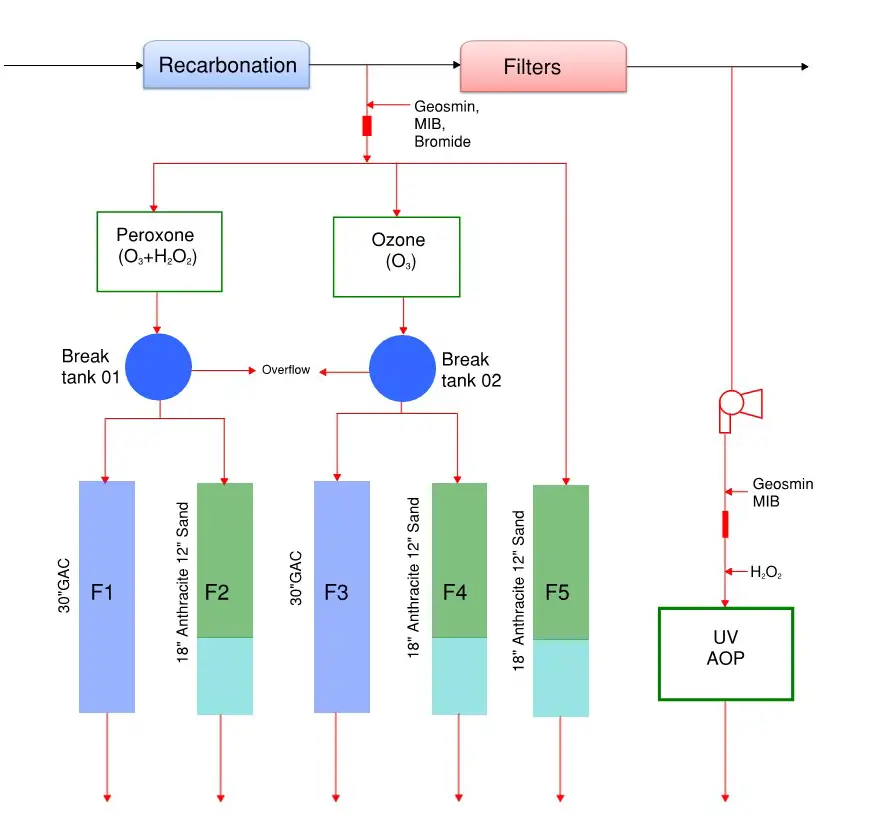
Pilot Study Protocol
A comprehensive pilot study protocol was developed to evaluate how advanced oxidation and biological filtration can be used either separately or together to remove T&O and mitigate DBPs treating Mississippi River water.
In addition to the online instrumentation data collection, a weekly water quality monitoring program was established to collect essential water quality data to evaluate the performance of various treatment processes. During the spring runoff period in 2016, the raw water TOC increased 150 percent in two weeks: a perfect organic storm. Samples were analyzed for a range of interested parameters: Geosmin, MIB-2, bromate, bromide, TOC, biodegradable dissolved organic carbon (BDOC), UV254, and Contaminants of Emerging Concerns (CECs). Simulated distribution system (SDS) tests were performed to evaluate DBPs formation through free chlorine disinfection and chloramines as secondary disinfectant in the distribution system. In addition to THHMs and HAA5s, N-nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA) were monitored as well.
Results
Both perozone and ozone can substantially reduce T&O compounds and achieved 80-90 percent reduction. Addition of H2O2 accelerates the formation of free hydroxyl radicals to remove T&O compounds, as well as reduced bromate formation potential. After AOP processes, T&O compounds were further removed through biological filters. Geomsin was under minimum reporting limit (MRL) for all four biological filters while MIB was reduced another 4-8 percent. Significant benefit was observed on DBPs formation through AOP and biological filtration. AOP oxidized unsaturated organics and converts to BDOC that was consumed by biological filters.The SCWTF advanced treatment technology upgrade is currently in discussion with a tentatively timeline of 2017-2018.