Potential Health Impacts
- Reproductive effects
- Developmental effects
- Effects on the immune system (antibody production)
- Increased risk of cancer
- Increased cholesterol/risk of obesity
Perspectives and Insights > PFAS
PFAS, or Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances, comprise a complex family of more than 10,000 synthetic chemicals that are widely used in everyday products due to their resistance to water, grease, and stains. These chemicals have been utilized for decades in a range of applications, including non-stick cookware, water-repellent fabrics, and firefighting foams.
Though highly valuable for these purposes, growing evidence points to potential health risks associated with PFAS exposure and their persistence in the environment. As they are commonly referred to as “forever chemicals,” due to their inability to break down naturally, concerns over their impact on both human health and the environment have led to increased scrutiny and regulation.
The United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has finalized the first ever drinking water regulations for six PFAS chemicals. The final rule sets a maximum contaminant level goal (MCLG) of zero and a maximum contaminant level (MCL) of 4.0 Parts per Trillion (ppt) for both PFOS and PFOA. The rule also sets individual MCLGs and MCLs of 10 ppt for PFHsS, PFNA, and HFPO-DA (GenX).
EPA also proposed a Hazard Index approach, as described below, toward the regulation of a mixture of four PFAS chemicals: PFHxS, HFPO-DA (GenX), PFNA, and PFBS. The finalized regulatory framework is based on running annual average of samples, which is similar to the compliance methodology for disinfection by-products.
Levels protective of health effects over a lifetime of exposure, including sensitive populations and life stages.
Ratio of potential exposure to a substance and the level at which no health effects are expected (HBWC).
Sum of component Hazard Quotients (HQs), which are calculated by dividing the measured regulated PFAS component contaminant concentration in water by the associated Health Based Water Concentration.
A hazard index calculation greater than 1 would trigger a violation and corresponding regulatory enforcement action.

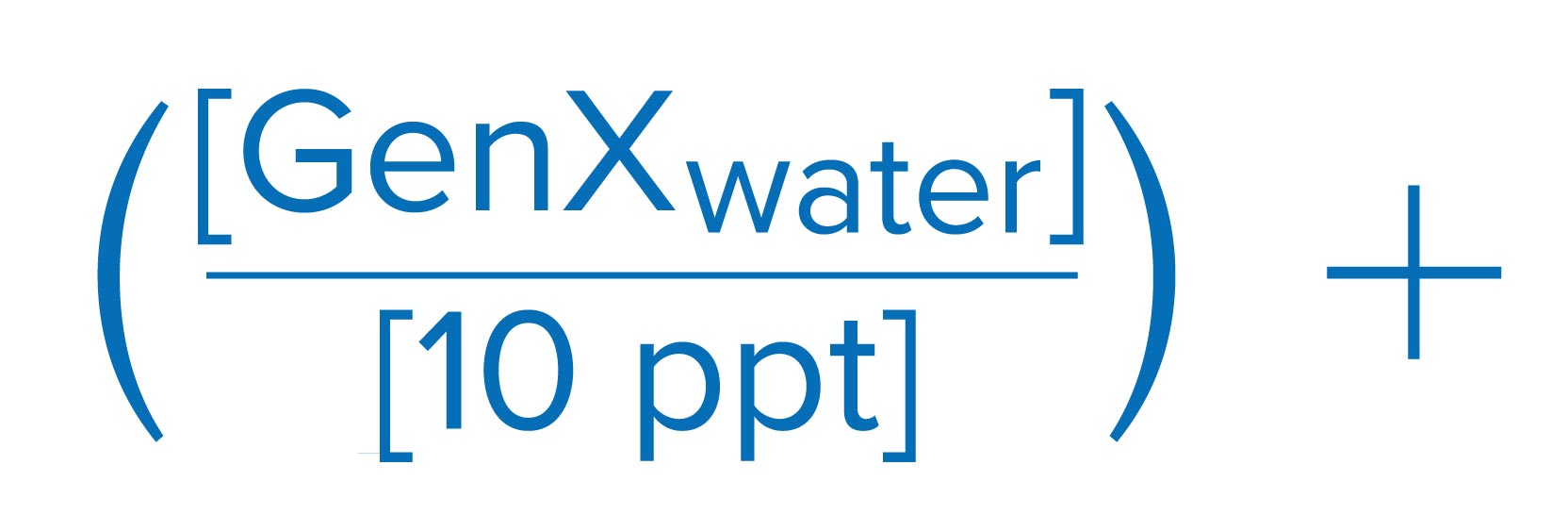
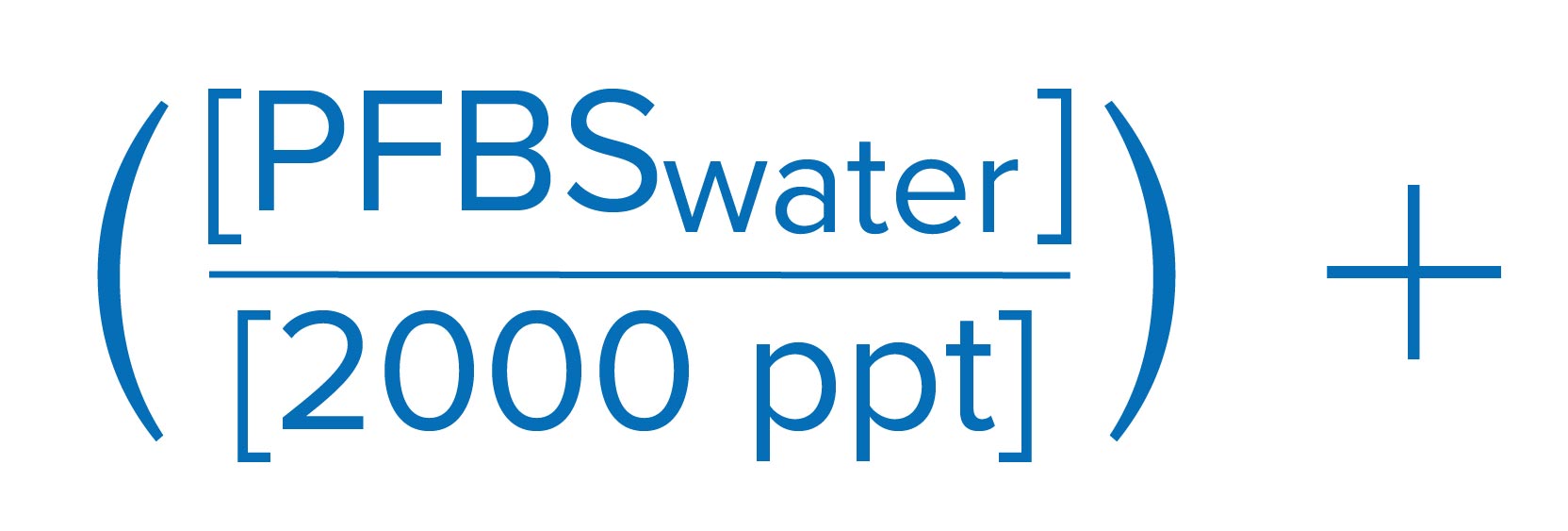

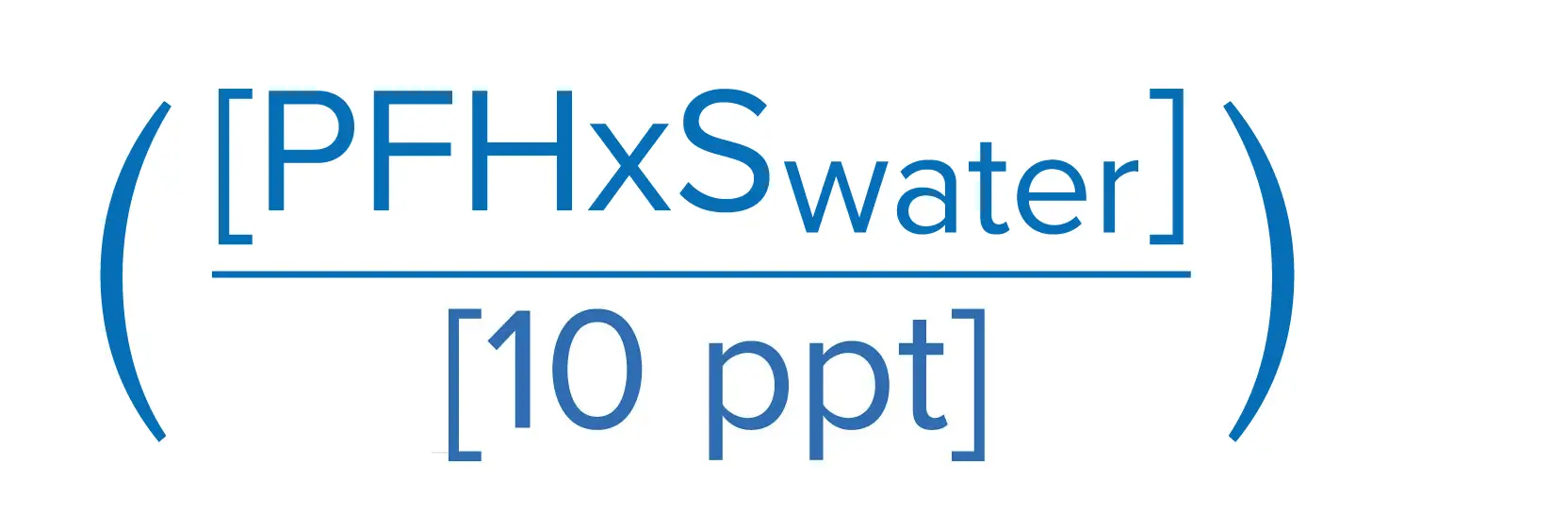
Considerations for selecting a treatment solution:
• Space available
• Pretreatment requirements
• Removal effectiveness
• Capital investment
• Operating costs
• Disposal of waste/media
Granular Activated Carbon (GAC)
PFAS compounds absorb to the porous carbon particles
Ion Exchange (IX)
Positively charged resins/polymers bind the negatively charged PFAS (and other) compounds
Reverse Osmosis (RO)
PFAS accumulating in treatment residuals also presents challenges. Options for treatment residuals are provided below:
Future regulatory actions not under the Safe Drinking Water Act (SDWA) may have a bearing on future disposal options.
The Update is a monthly newsletter exclusively focused on U.S. water news, encompassing regulatory compliance and political developments.
